
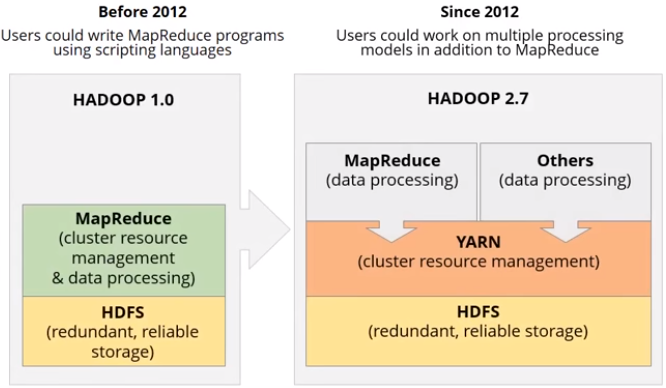
YARN stands for Yet Another Resource Negotiator. It was introduced in Hadoop version 2 to extend other data processing framework to not only Map Reduce such as Spark, Storm, etc.
Yarn help to manage Hadoop cluster with:
- Higher cluster utilization: resources on free node will be consumed by another
- Lower operation cost: all cluster will be managed on single hub as YARN
- Reduce data motion: no need to move data between Hadoop YARN and system running on different cluster of computers
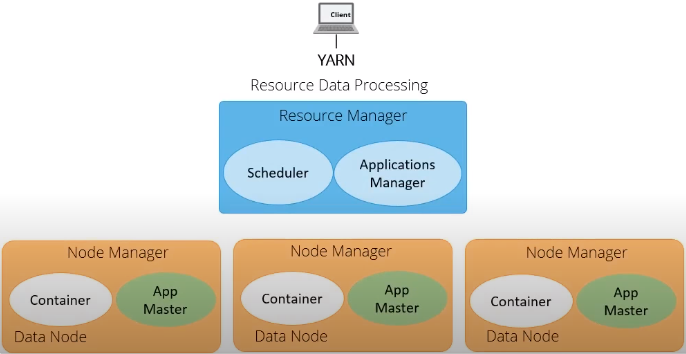
Resource Manager
- RM is the master server and running difference services including Scheduler and Application Manager.
- It knows the location of data nodes and how much resources they have.
- Scheduler:
- Allocate resources to various running applications
- Constraints based on: capacity, queue, etc.
- Not monitor or track status of application & not restart failed tasks
- Policy Plugins: CapacityScheduler, FairScheduler, etc.
- Application manager:
- Maintain list of applications submitted, running or completed.
- Accept job submission, negotiate first container for executing the application and restart application master on failure.
- From Hadoop 2.4, RM is featured with Active/Standby Resource Manager pair to avoid single of failure (only one single master node)
Node Manager
- Can be many in one cluster
- Once started, it announce itself to RM and offer resources (RAM, vCores) to the cluster.
- It periodically sends heart beat to RM
- Each node take instructions from RM, reports and handles containers on a single node.
- Once a container is leased to an application, the NM setup container’s environment including resource constraints in the lease and any dependencies.
Application Master
- Framework-specific library
- Negotiate resource for a single application that is a single job or directed acyclic graph of jobs.
- Manage application life cycle and task scheduling
- Provide status & metrics to RM
- Not run as trusted service
- Act as an instance for a single application or set of applications
Container
- Result of a successful resource allocation, that is RM has granted an application a lease to use specific resources on a specific node
- Application master provide Container Launch Context (CLC) that includes following information:
- Environment variables
- Dependencies
- Security token
- Necessary commands to create the process for application to launch
- Therefore, there can be many workload types can run on Hadoop Yarn cluster like MR, Tez, Hbase, Storm, Spark, etc.
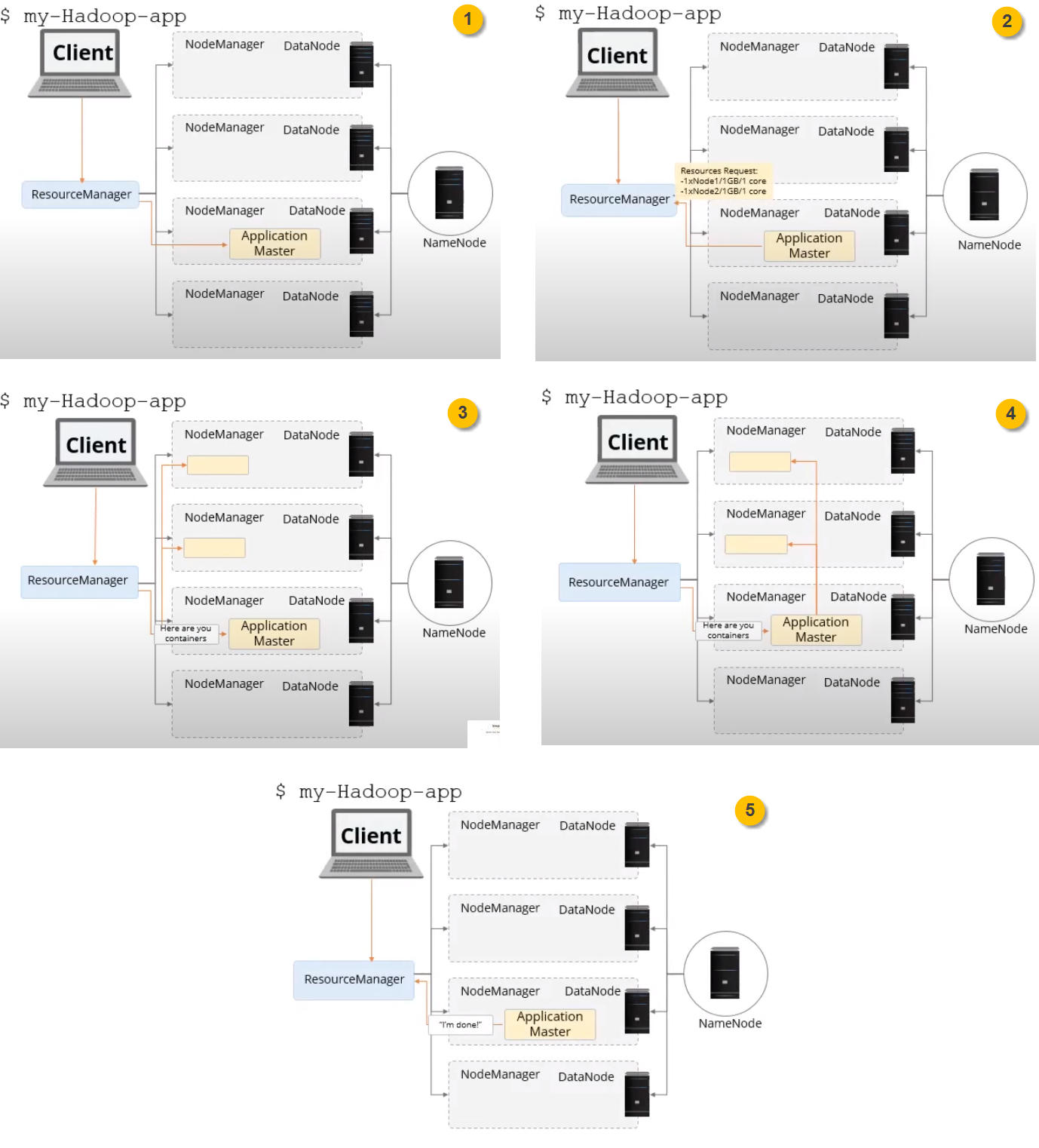
How it works?
- Client submits job (via HUE [Spark, Hive script on Oozie workflow scheduler], Zeppelin or YARN CLI) to Resource Manager which will be then assigned to one node manager
- Application master requests resources to run the application
- RM assign resources which will initialize containers on available nodes
- Application master will run the application on assigned containers
- Application releases container once job done and finish the life cycle
Comments